The advent of computer-aided design has its origins in the 1980s with the advent of the first PCs. In these 40 years, the digital transformation of professions has been increasingly vertical and today we do not speak of 3D models, but of Information Models from which to extract and manage innumerable data related to the AEC process.
Driven by the need to improve efficiency, reduce costs and increase the sustainability of projects, the construction industry is experiencing a digital revolution. The digital transformation in the AEC sector on the one hand offers numerous advantages in terms of accessible data and available software, but on the other hand also highlights obstacles concerning their dialogue and compatibility in the operational environment: in a word, ‘interoperability’.
In this context, INCIDE Enigineering has for some time now been working in partnership with universities and has set up its own R&D (Research and Development) area through which to improve its BIM-assisted design processes and develop applications dedicated to the entire construction supply chain.
Let’s get to the heart of the matter to understand the obstacles of limited interoperability and the concrete solutions to develop it and enjoy its advantages in civil and industrial design.
The issues of limited interoperability
To meet the needs of different disciplines, the market offers many software tools, both BIM and non-BIM, to develop projects. However, one of the main obstacles designers face is the limited interoperability between the different tools used, as it is not always possible to have an application that allows dialogue between them. In particular, since not all software integrates the VPL, a way must be found to export what is produced with them to other software.
Each discipline involved in the project may use different tools, and the lack of communication between these software may generate these problems
- loss of information during data transfer
- delays in managing changes;
- difficulties in controlling the material produced.
The consequences of these obstacles are reflected in sub-optimal use of resources and increased project costs. How, then, to make the best of the digital transformation?
How to develop interoperability: INCIDE Engineering’s solution
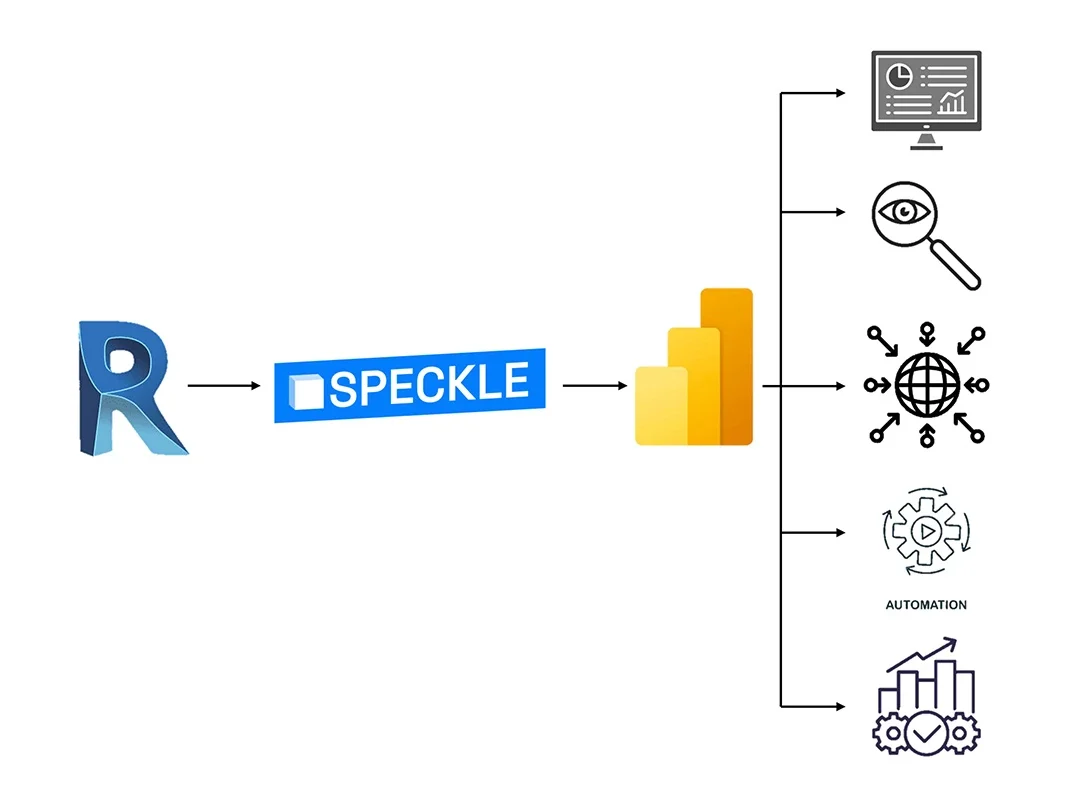
To overcome these challenges, INCIDE has integrated the Speckle tool into its workflow, an open-source platform designed for data sharing and collaboration in design and construction projects. The adoption of this tool offers numerous advantages, including:
- the ability to upload and download elements from the software used directly into the platform, free of charge;
- integration between software, as tools such as Speckle allow programmes such as Revit, Rhino and AutoCAD to be connected, facilitating the exchange of data between them;
- real-time collaboration between teams that can work simultaneously on the same models, ensuring immediate synchronisation of changes;
- open and transparent data: models, geometries and information can be easily managed and shared, providing greater transparency in design processes.
Let’s see this methodology in action with a practical example.
Managing complex geometries: a case study
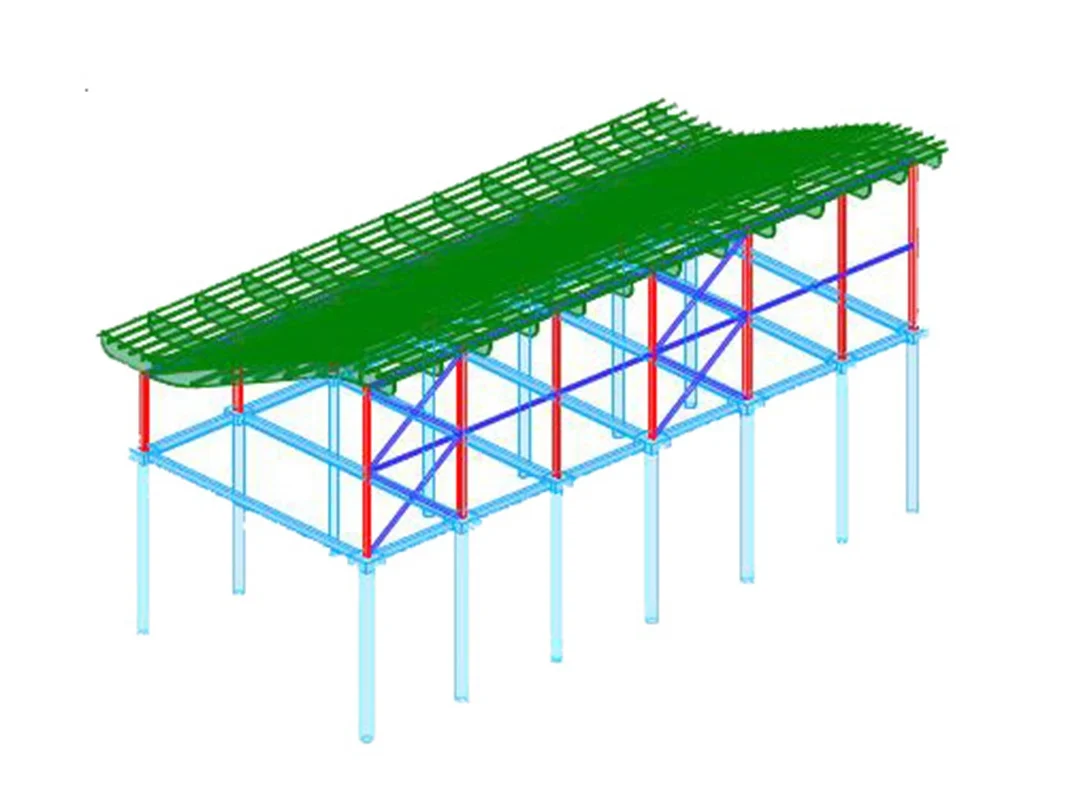
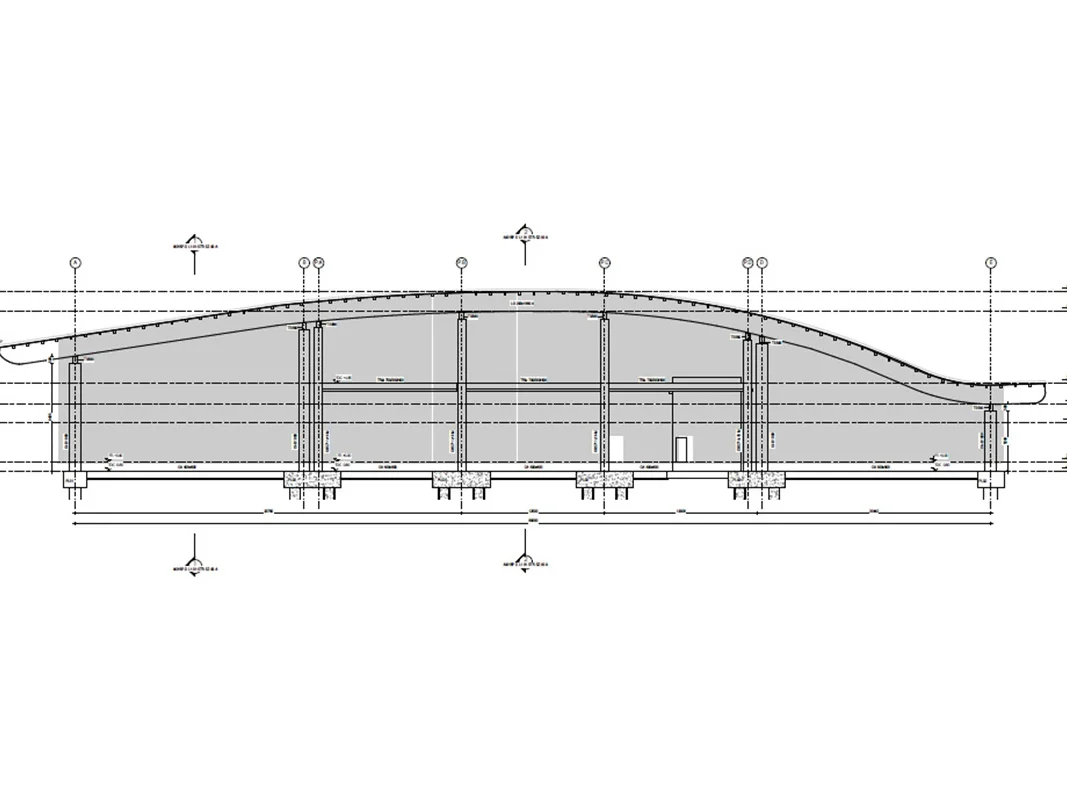
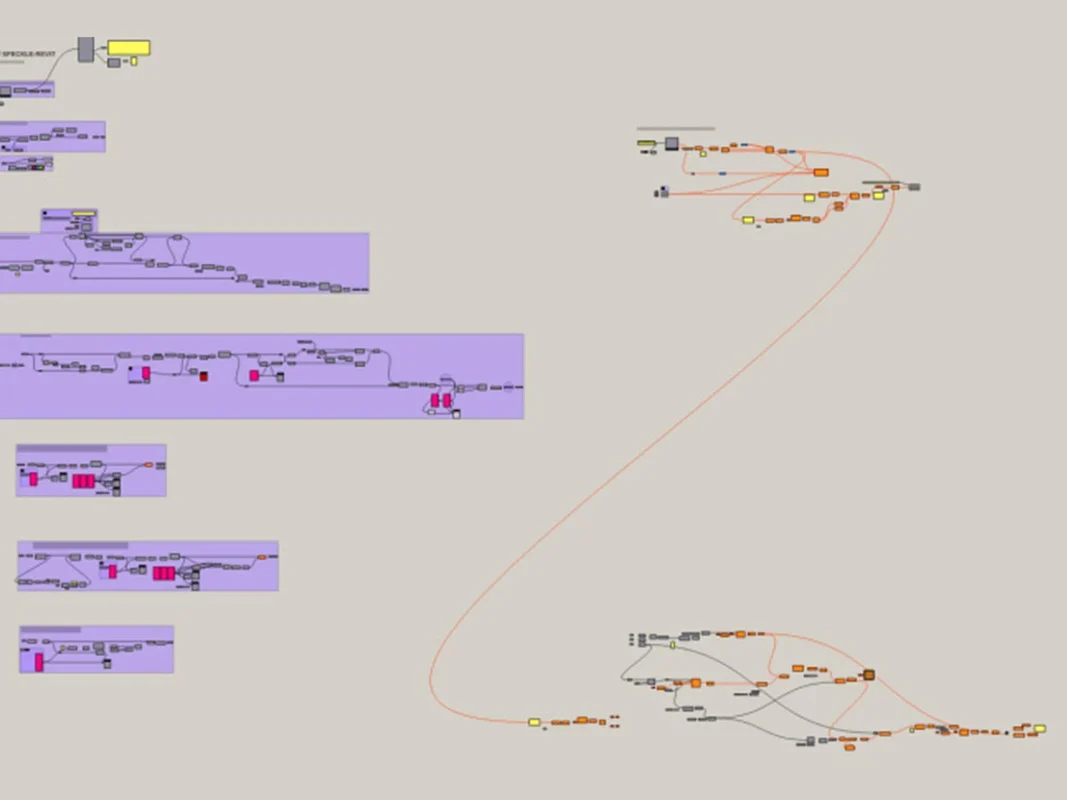
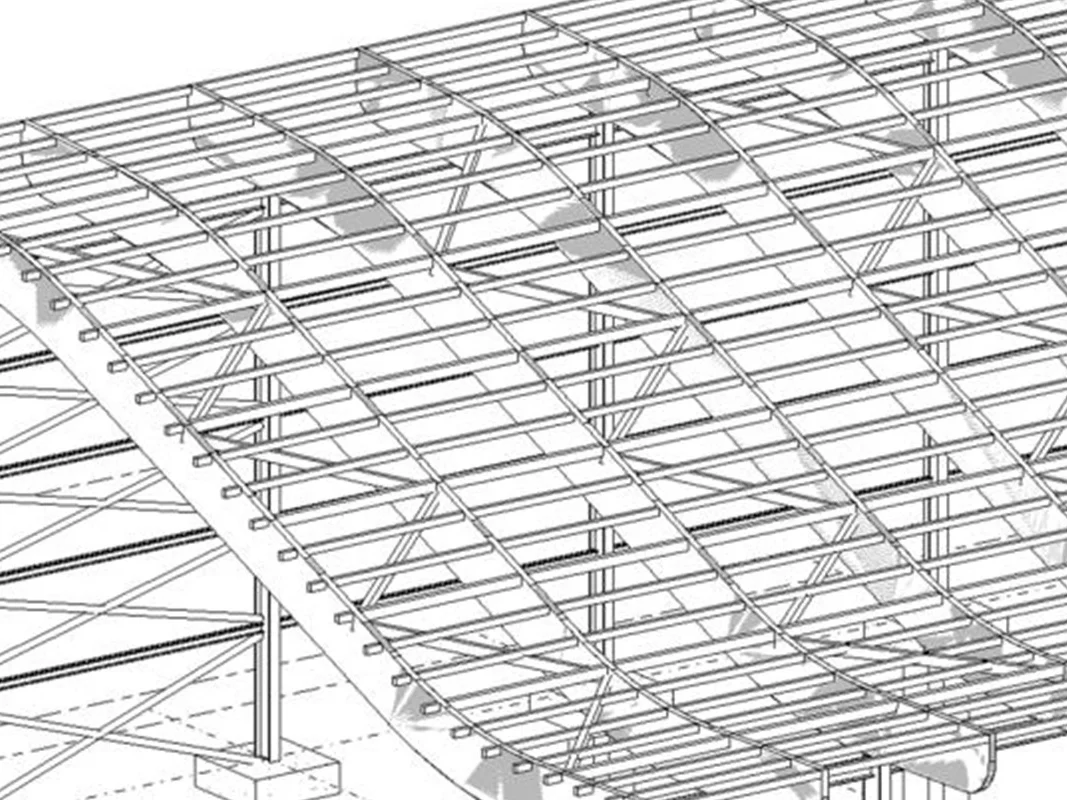
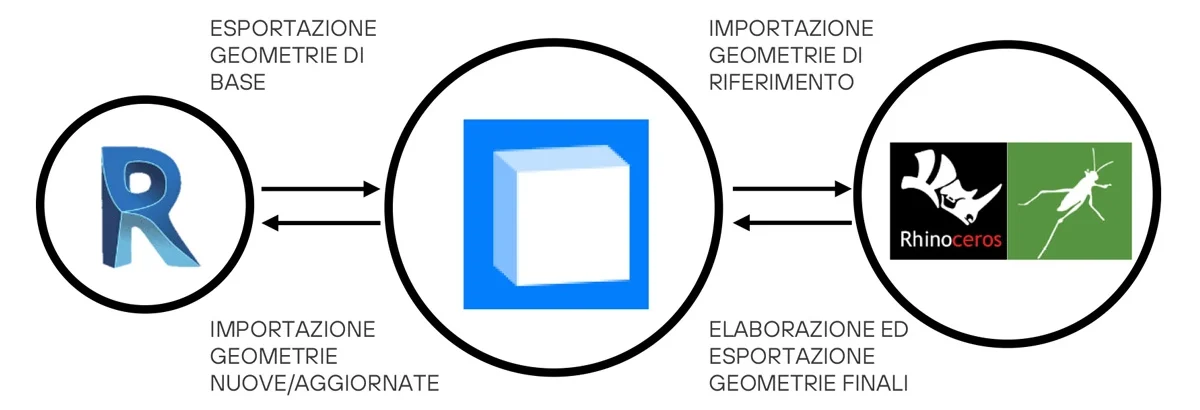
A practical example of the use of Speckle is the project developed by INCIDE of a complex roof structure with curved wooden main beams , with secondary beams and bracing in line with the profile of the main ones.
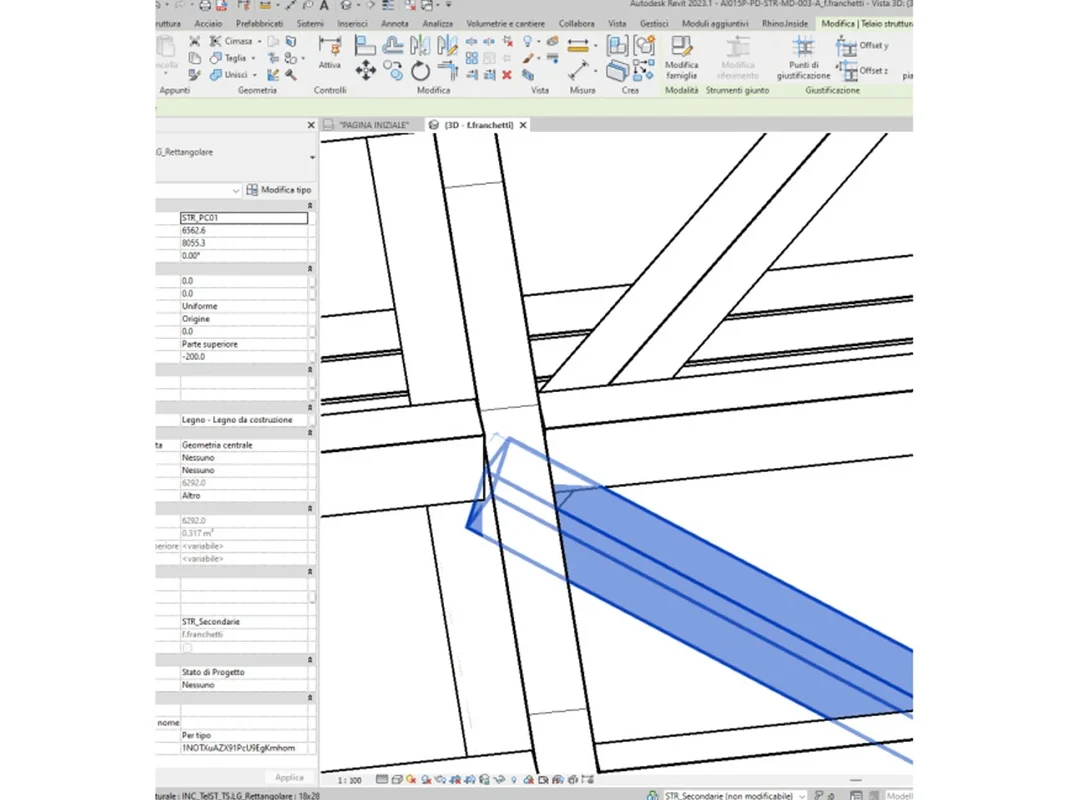
The traditional modelling presented several difficulties, such as the manual positioning of the secondary beams in Revit, due to the impossibility of adequate management of the intersections of the axes with that of the main beams; in addition to this, there was also the impossibility of setting up a series of beams subject to updating of the elements as the parameters changed.
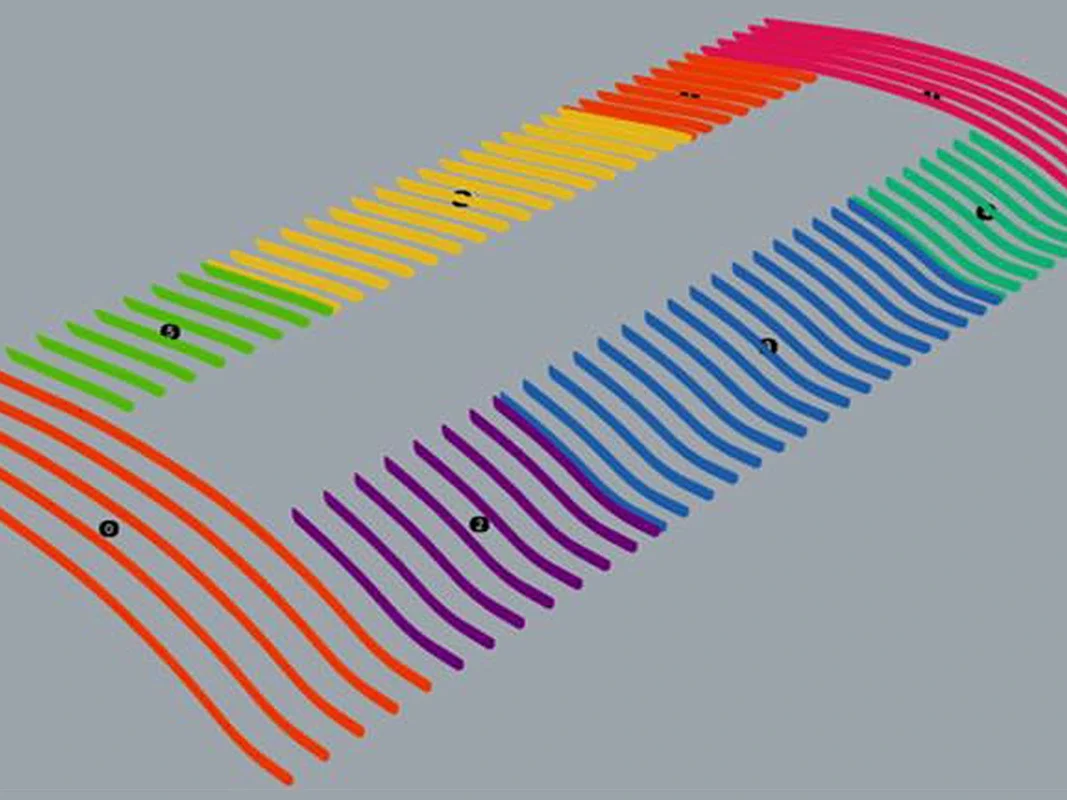
Thus, through the use of Speckle, it was possible to import the geometries of the secondary elements modelled precisely on the basis of rules by Grasshopper into the Revit model.
In particular, information on the main beams modelled in Revit was uploaded to Speckle, which was used to transfer the main geometries of the model from Revit to Rhinoceros. The latter, after importing the geometry from Speckle, using it as input, generates the secondary elements with the help of Grasshopper. Finally, the updated data were reloaded onto Speckle, allowing Revit to read them and integrate them back into the final model.
Through the integration with Rhino and Grasshopper, it was then possible to
- import the geometries of the main beams into Rhino;
- accuratelymodel the secondary elements using Grasshopper scripts;
- export the final geometries to Revit using Speckle.
This methodology greatly simplified the process, improving efficiency and reducing the margin of error.
Intelligent model analysis and management with Power BI
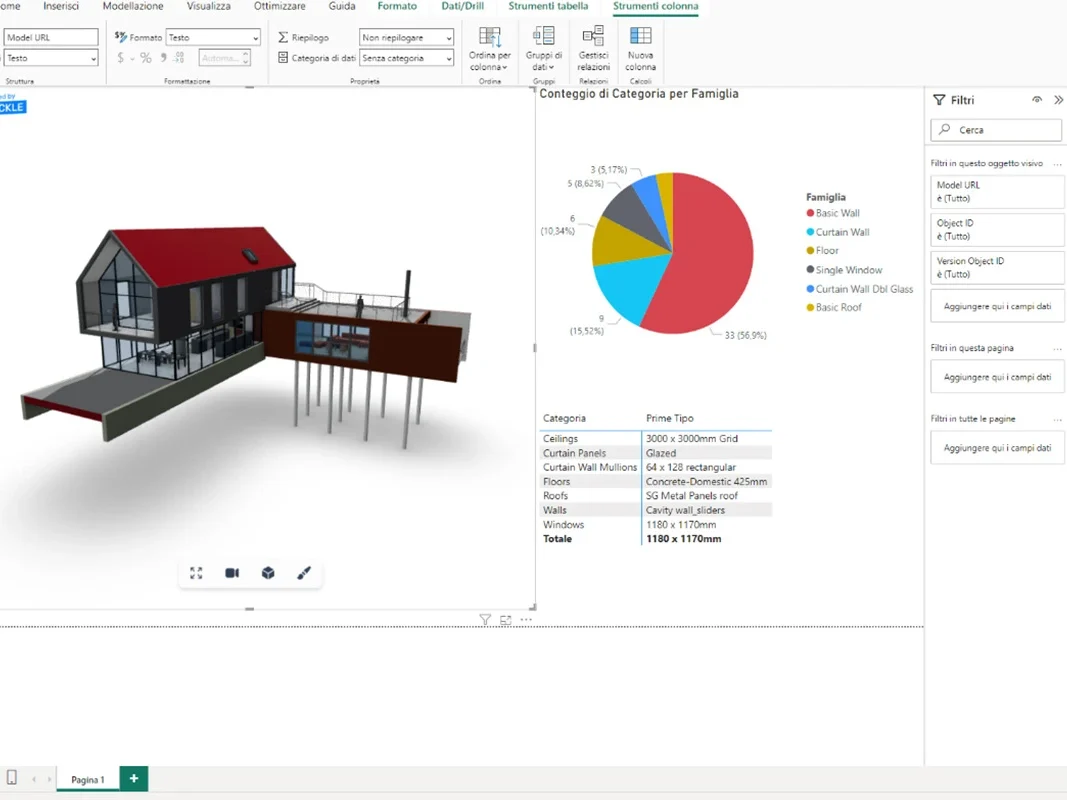
INCIDE Engineering has also integrated Microsoft Power BI with Revit via Speckle. This is a data analysis tool that creates interactive dashboards and visual reports. In the context of project management, the interaction between these tools enables intelligent management of BIM models, because it allows you to
- create customised dashboards that combine project data with other enterprise data sources;
- provide intuitive visualisations of BIM data for better analysis and understanding;
- centralise data from multiple Revit projects, improving overall management and insight;
- automate data extraction, transformation and loading processes, reducing manual work and errors.
All of this contributes to improving operational efficiency by analysing project data to identify and resolve inefficiencies in a timely manner.
Collaboration becomes more effective with interoperability
As it emerged from this working method and the practical examples illustrated, the digitisation of design processes is essential to meet modern industry challenges.
With the adoption of innovative tools such as Speckle and Power BI, INCIDE Engineering uses effective solutions to improve interoperability, reduce costs and optimise project management. These technologies not only accelerate execution times, but also ensure greater accuracy and transparency, enabling effective collaboration across teams and disciplines.