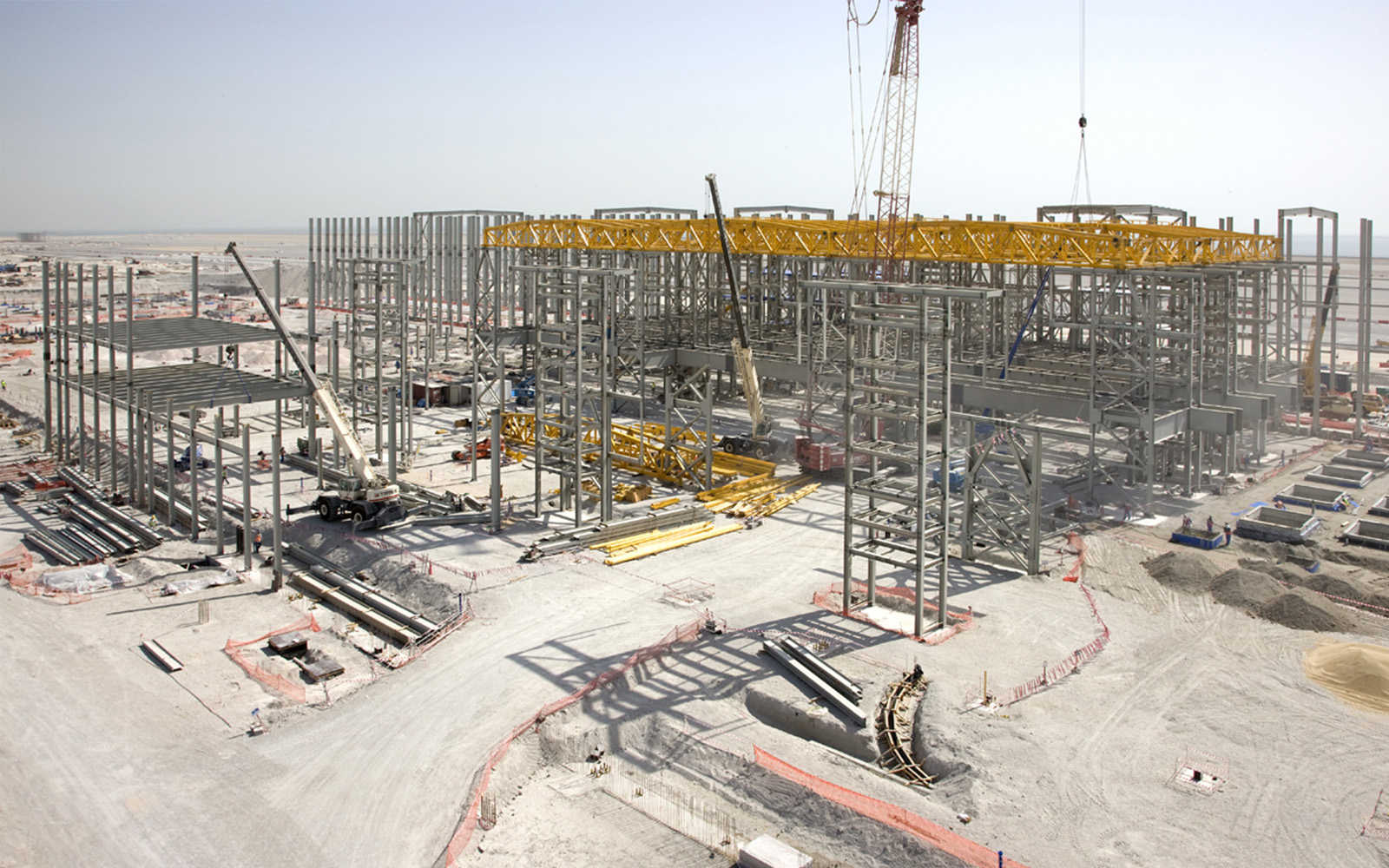
In the world of civil engineering, structural steel is an essential element in the construction of durable buildings. Its use in construction revolutionised the entire industry, as the history of steel and the completion of the Brooklyn Bridge in the 19th century suggests. The protagonist of increasingly innovative uses, structural steel has many advantages in different areas, thanks to its properties.
Look in detail at all the benefits of this material, its mechanical properties and its usefulness in seismic areas.
The mechanical properties of structural steel
The steel used in steelwork is a homogenous, isotropic and isoresistant material. It’s characterised by a number of important properties:
- strength;
- ductility;
- dissipation;
- versatility;
- high mechanical performance.
The classification of structural steel is based on its chemical composition, while its specific characteristics and applications are defined by standard UNI EN 10027-1, which establishes alphanumeric designation systems for the various types of steel.
The mechanical, physical and chemical characteristics of steel are also determined through material qualification tests, such as the tensile test, resilience test and chemical analysis.
Finally, the material’s deformability, stability depending on use and fire protection must be checked. To meet these checks, safety checks are regulated by the NTC08 and Eurocode 3 standards.
The mechanical properties of structural steel give rise to important advantages that make it versatile and useful in various construction fields.
The advantages of steel construction
The dry construction system is based on a wise approach to building construction that can meet high performance standards in several areas, such as seismic safety, durability, eco-efficiency and many others.
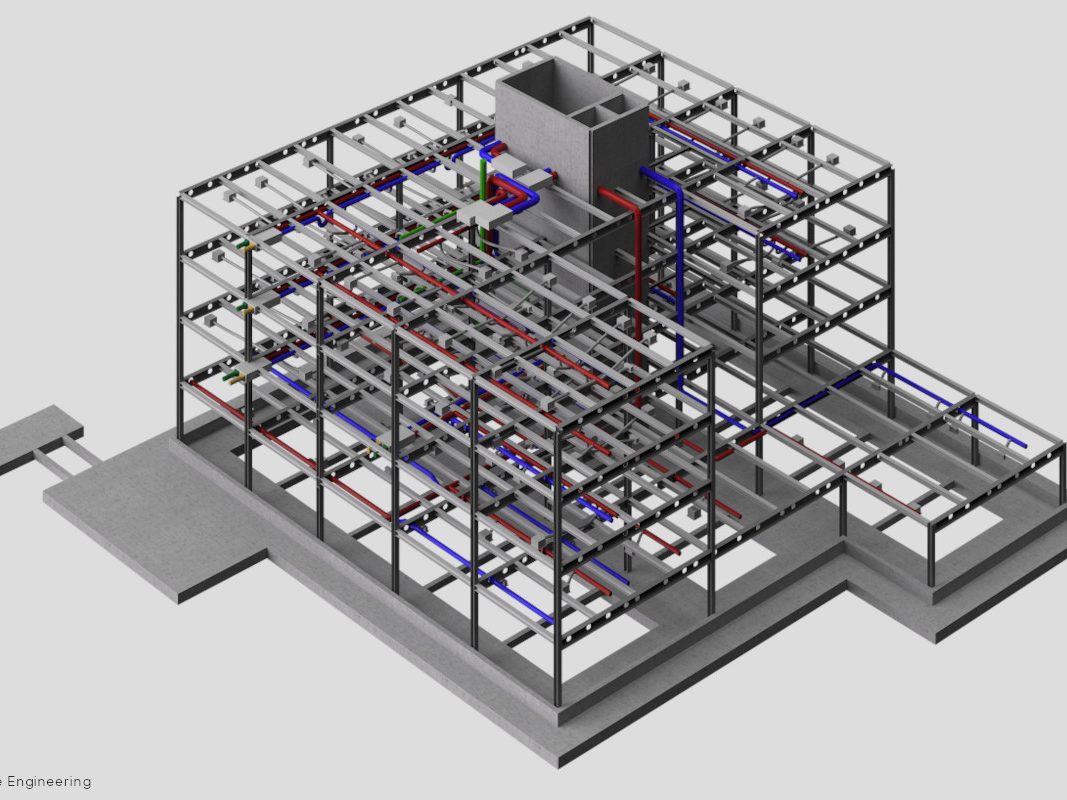
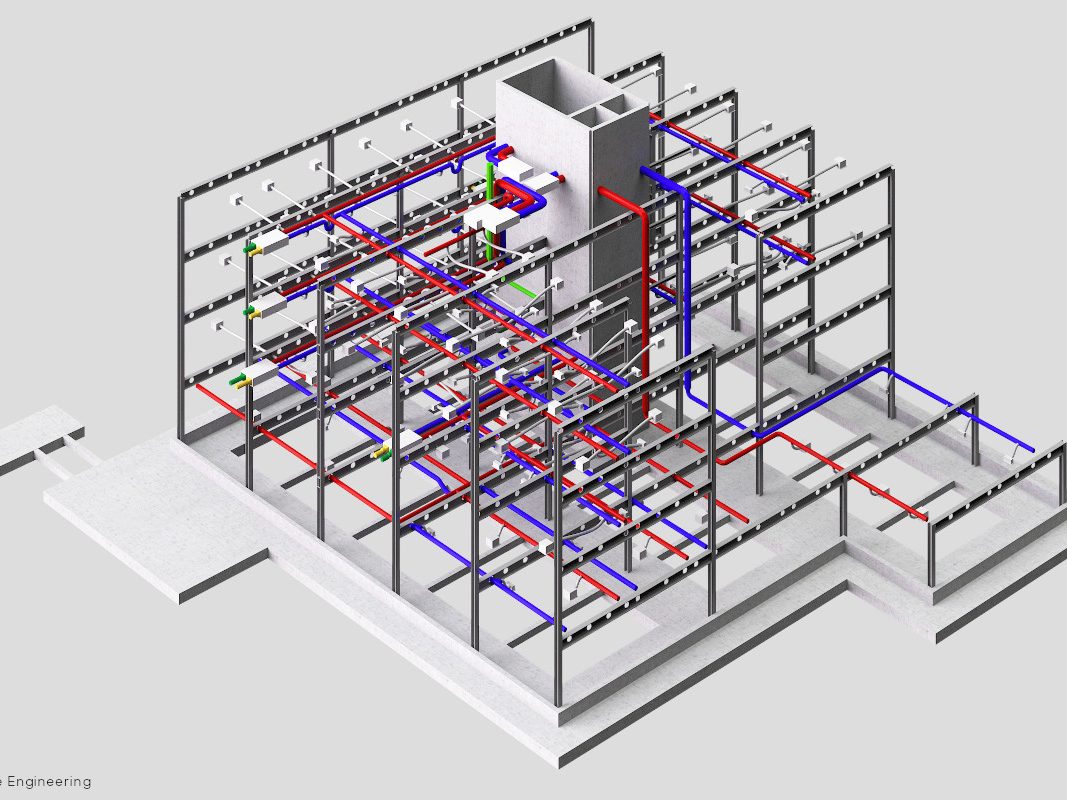
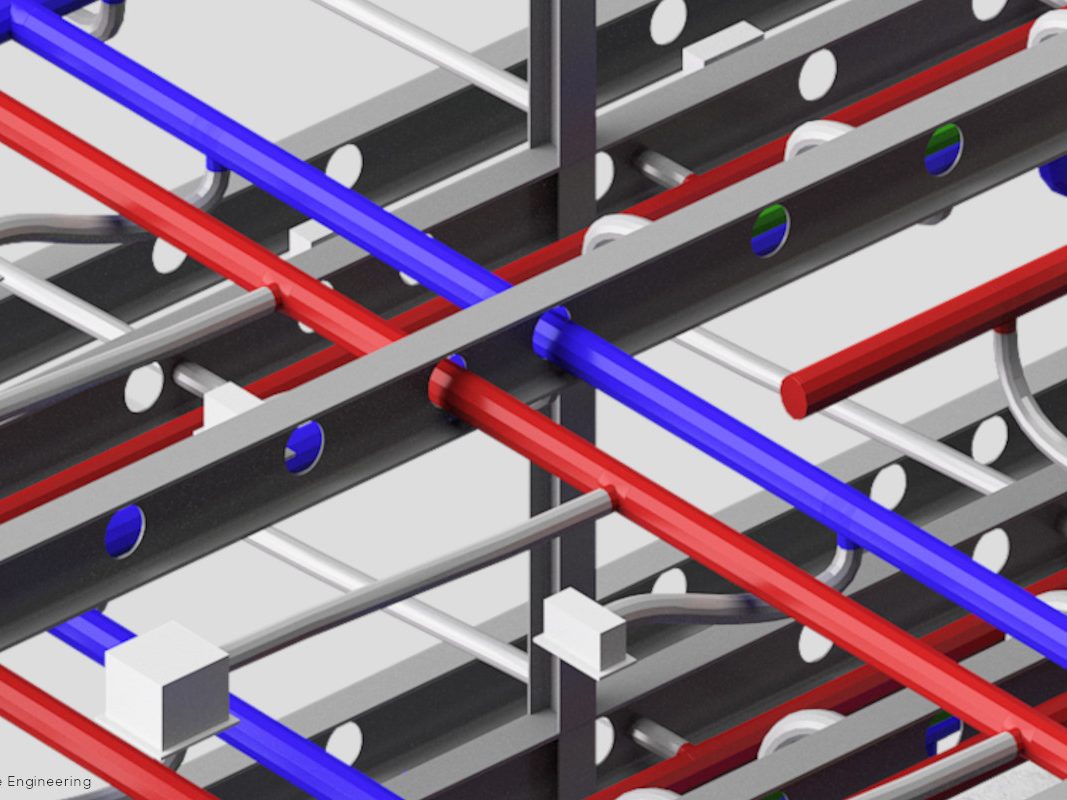
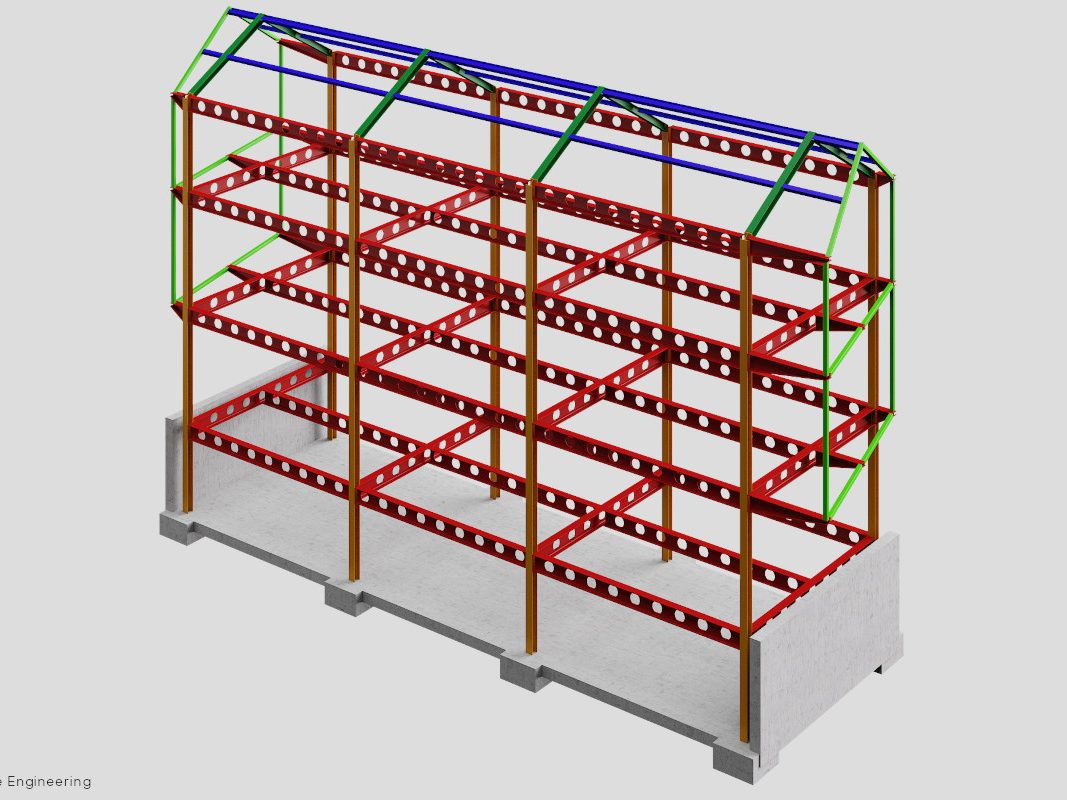
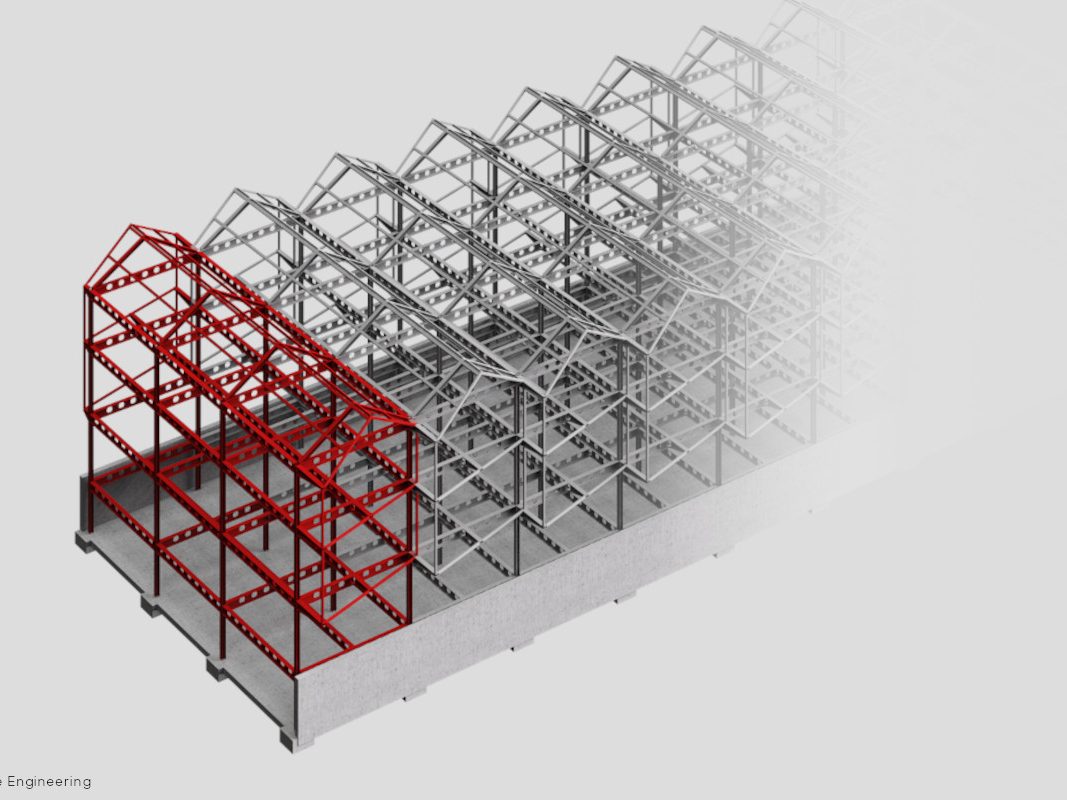
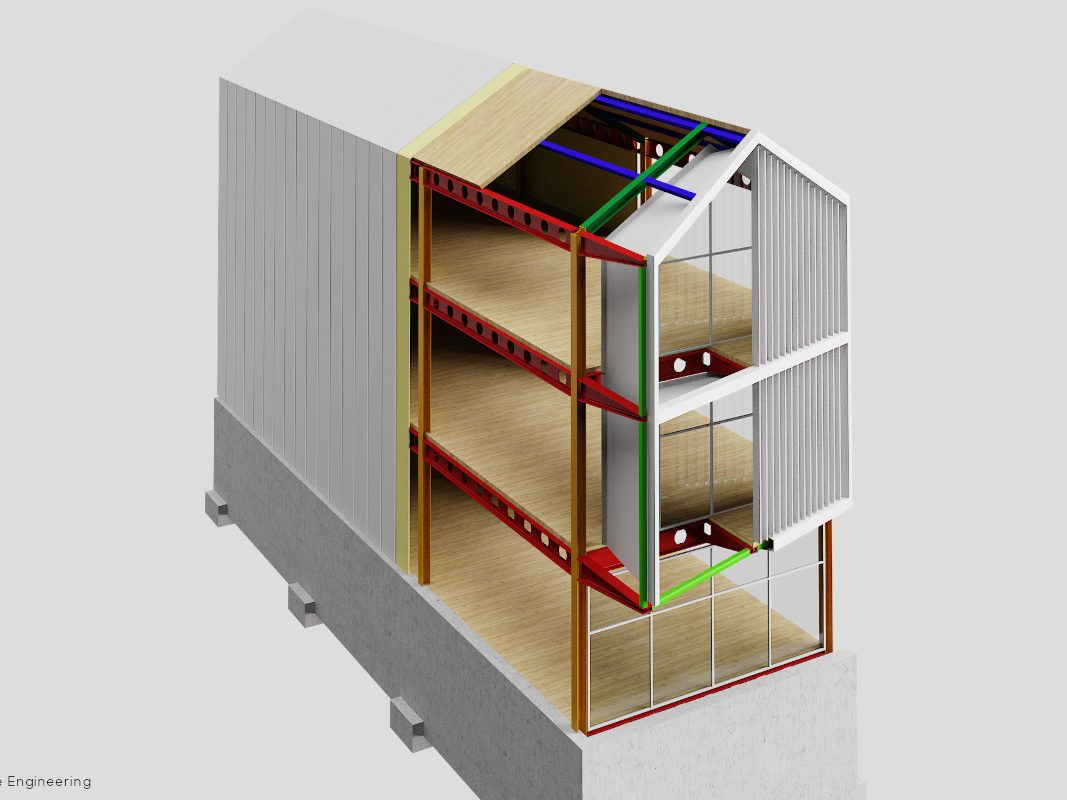
Steel constructions make it possible to consciously draw on the heritage of industrial production related to construction to create highly technological and sustainable artefacts. These buildings, conceived in a similar way to machines, are born from the combination of various materials and layers that, each for their own characteristics, contribute to the desired performance sum; they are characterised by steel frame structures to which planar, light, thin and large elements such as sheet metal, sandwich panels, slabs of various types and insulating mats are attached. These features conceal important benefits: these are the advantages of steel constructions.
Reduced lead times
The high level of prefabricability and ease of assembly of steelwork allows finished solutions to be realised in a very short time. The dry steel system, in fact, allows a precise management of construction time, a reduced use of resources, and a drastic reduction of waste materials. Thanks to the industrialisation of the building process, all structural elements and envelope systems are manufactured off-site, taking into account subsequent assembly operations. In this way, they are already ready for installation, with extreme ease of assembly: construction time is thus cut by 50-60%. In addition, the daily problems and long drying and curing times for plasters and screeds typical of the traditional building site are eliminated.
Comfort, healthiness and durability
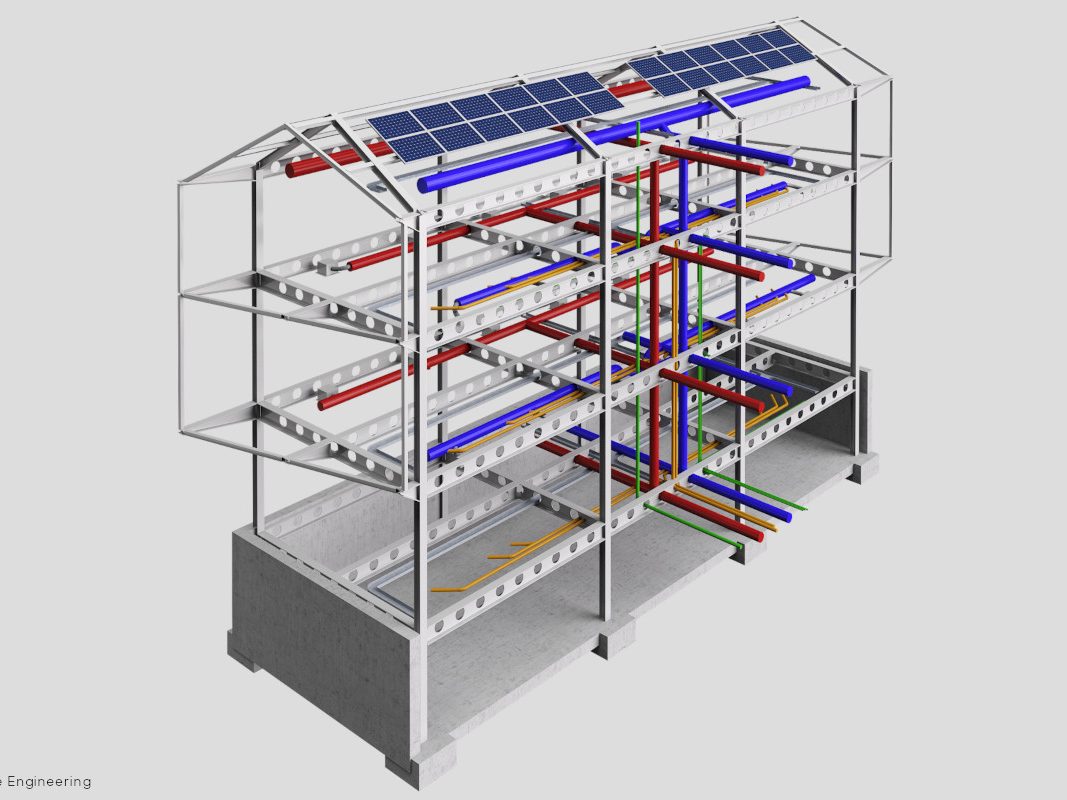
Thanks to the technical-constructive measures applicable to steel construction and the materials used, it is possible to achieve very high energy performance for Class A buildings. High thermal-acoustic insulation ensures the quality of the indoor environment.
Plants, such as heating and/or renewable energy systems, are also easily integrated into the structure. As steel is not a conductor of moisture, it guarantees healthy environments without the so-called ‘sponge effect’. Steel solutions do not require maintenance and the treatments to which the profiles used are subjected guarantee anti-corrosion with consequent durability of the building.
Fire resistance
Buildings made of steel have a higher passive fire resistance than other industrialised construction systems using other building materials. The steel structure is almost always placed within cavities that already contain insulation, such as plasterboard sheets, which provide excellent fire protection. In the event that there are other requirements, however, it’s possible to use special sheets that achieve very high parameters of fire resistance. The steel structure can then be treated for fire resistance according to specific requirements: if this is left exposed, a protective treatment can be carried out.
Sustainability
The environmental impact of a steel construction is reduced both during the construction phases and at the end of the building’s service life, thanks to the high recovery rate of the components, which are mechanically assembled and not wet-assembled. Furthermore, the industrialisation that characterises the dry steel solution guarantees:
- overall energy reduction for the same built square metres compared to other building solutions;
- reduction in packaging and waste; possibility of reusing building components;
- no use of raw materials: the steel used in construction comes from recycled material;
- increased safety at work;
- reduced transport of both goods and labour;
- prevention of climate change.
The CO2 emissions for producing and processing steel products in the workshop account for less than 3% of the total national greenhouse gas emissions and recycling: steel is the most recycled material in the world and is 100% recyclable, it can be recycled countless times without losing any of its original properties.
Flexibility, modularity and easy disassembly
The versatility offered by the steel system allows for modularity and replicability. The characteristics of the building are adapted to the construction site and customisation to the functionality, and the design of the different finishes and façade systems. Moreover, in view of future new requirements and changes of use, the steel construction system is optimal for building extensions and elevations. Easy to dismantle and recycle at the end of its life.
Site management
The construction site of a steel building employs skilled labour. Assembly in the workshop allows for much more organised construction sites than those for buildings constructed using other traditional technologies, as these are industrialised structures, for which the work on site is limited to the assembly and fitting of construction components. It is also possible to intervene in confined spaces and unfavourable conditions. This makes it possible to realise not only ex-novo interventions but also extensions, superelevations or renovations with minimal impact.
In addition to these obvious advantages, there are two crucial aspects concerning production costs and seismic safety.
Steel construction in seismic zones
Steel has undoubted benefits related to flexibility and lightness: seismic forces are associated with inertia and dependent on the mass of the building.
Structural systems based on very ductile materials, such as steel, are able to withstand earthquakes and are much more advantageous than those based on less ductile materials, such as reinforced concrete and masonry.
In very high seismic conditions, the structure’s lightness and ductility guarantee high levels of endurance and any restoration and maintenance work will be zero or minimally invasive, unlike more rigid structures, such as those using concrete, which are difficult to monitor after the earthquake.
Dry connected envelope systems, with connections capable of supporting displacements during an earthquake, offer considerable advantages that also limit possible damage to non-structural components.
The construction cost of a steel structure
The speed of construction, together with the optimised design, results in a reduction of financial burdens. Furthermore, thanks to the mechanical characteristics of steel profiles, much lighter structures are obtained and there is a reduction in costs concerning foundation works, excavation and casting volumes, as well as a reduction in emissions due to the transport of supporting structures and materials in general.
Another fundamental aspect is that the incidence of labour is also lower: activities carried out on site cost considerably more than activities carried out in the workshop.
Steel structures design: Incide’s solutions
Incide Engineering combines high competence and professionalism with a constant focus on new design techniques and methodologies for structural engineering.
In the field of steel structures, its many decades of experience is manifested in a deep understanding of the challenges and opportunities presented by these buildings.
Through its method, Incide accurately covers conceptual design and the development of calculations using finite elements, the production of executive and construction drawings using BIM methodology, benefiting from the interoperability of processes, and the study of assembly phases.
These are just some of the services that Incide offers in the field of structural engineering, ranging from special steel structures (port cranes for loading and unloading, special structures for industry, silos, boilers and industrial chimneys), reinforced concrete structures and tensile structures.
The steel structure projects carried out by Incide are numerous, but some of the most notable include interventions
- in sports, such as the Défense Arena, a multi-purpose facility in Paris or the Seine Musicale;
- for industrial facilities, such as the New Safe Confinement for the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant;
- for commercial buildings, such as the Aspire Tower in Doha, Qatar;
- for infrastructure, such as the Al Raha Bridge in Abu Dhabi;
- in the Aviation sector, such as the Cargo Terminal at Doha Airport.
Thanks to its certified experience, Incide is able to tackle the great challenges of structural and plant design in many sectors.
For more information, please contact us.