Deloitte, one of the world’s largest analysts and consultants to businesses, recently published the Report “Sustainable Buildings: Designing, building, and operating to help create a greener future” focusing on sustainable engineering and construction. In this article we will take a look at the main findings of Deloitte’s Report 2023 and find out how Incide Engineering is already actively meeting the needs of the environment and the market through increasingly sustainable design.
How to reduce our impact on the natural world within realistic spending limits
Worldwide, the built environment is responsible for 39% of gross annual carbon emissions: this includes all carbon emitted during the production, transport and disposal of construction materials. In addition, it’s becoming increasingly common for architecture, engineering and construction companies to receive requests from clients to reduce the amount of carbon used in construction projects: in the US alone it’s more than 90%, a survey by Dodge Construction Network shows.
The expense required to realise this vision can be considerable for a company’s finances, but the cost of a high initial investment can be offset by decisive long-term benefits.
Deloitte’s report outlines various starting points, recommendations and useful approaches to begin to achieve your own and your clients’ sustainability goals, within the limits of realistic expenditure: let’s look at the main ones.
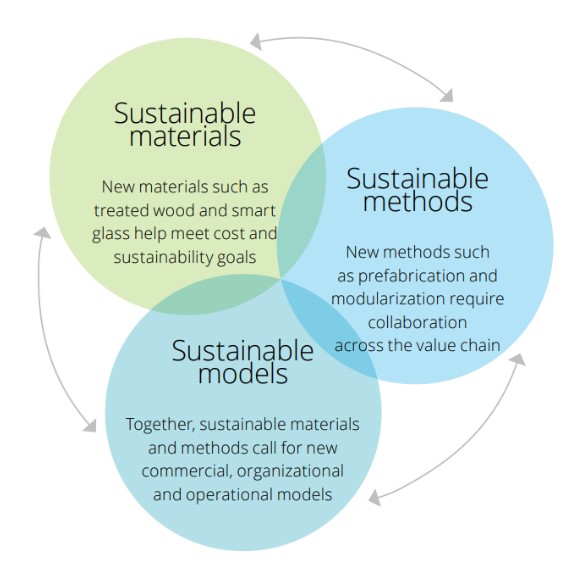
The triad of sustainability
There are already elements that guide the industry in its progress towards reducing emissions.
In particular, sustainability is achieved through some central factors such as materials, construction methods and business models.
Source: Sustainable Buildings Report, Deloitte, 2023
Sustainable materials
The use of sustainable building materials reduces construction costs and, due to their durability, the finished building requires less maintenance, especially for high-performance façades.
In addition, there’s been a general trend of reduced design and construction costs associated with sustainable buildings, as building codes become stricter globally, supply chains of sustainable materials and technologies evolve, and the industry becomes more adept at creating sustainable buildings.
Some examples that can reduce emissions by around 46% are:
- Replacing wood cladding with polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or water-resistant polypropylene resin to reduce the need for frequent repainting;
- The use of treated wood to emulate plastic or glass. It is lightweight, stores heat and reduces energy consumption;
- The installation of windows with smart glazing that can vary heating capacity depending on the amount of heat and air conditioning inside the building;
- Exploiting low-carbon bricks using 40 per cent fly ash or green concrete replaced by fly ash and granulated blast furnace slag.
The current deficit of the ecological supply chain is the lack of attention to material consumption, which makes it, more often than not, ineffective. During design and construction, it therefore becomes essential to use as few materials as possible (direct eco-sustainability), given the limited resources in the world, and to choose low-polluting production processes to favour proper disposal. It’s from this principle that Crossed Spirals® was born: a structure with crossed spirals, thanks to the idea of Enrico Rosasco’s architectural studio and the engineering of the architectural concept carried out by Incide Engineering: the mission is to create a sustainable solution that preserves the environment and is, at the same time, extremely effective.
Source: Crossed Spirals®: innovative structural solutions, Incide Engineering
Design and construction sustainable methods
Sustainable methods are another key element in meeting the challenge of green building. In this case, prefabrication and modular construction is a valuable aid. These methods not only reduce labour costs, but also ensure better control of the design, to shorten timescales and minimise budget overruns.
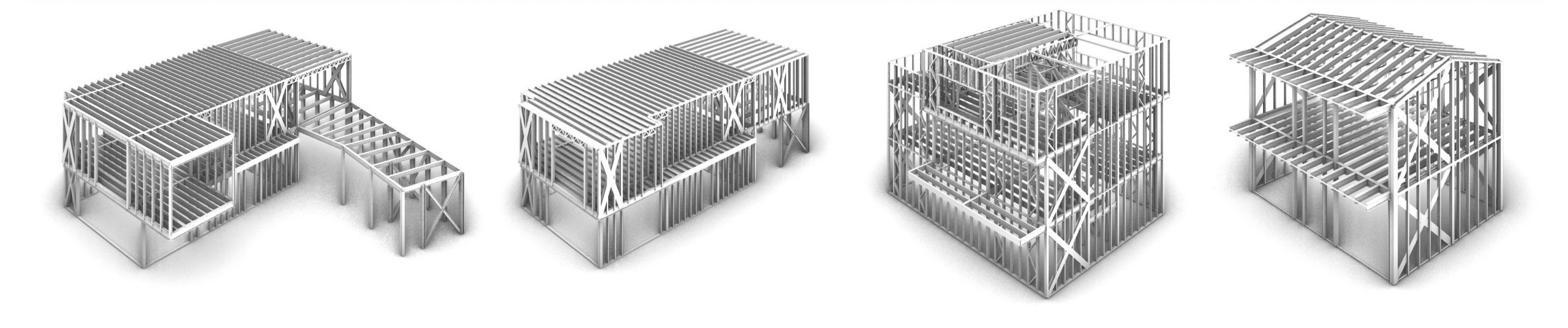
Incide Engineering has long been studying such solutions as the Light Steel Frame, which is also used for residential buildings. In fact, steel houses represent a new and growing construction system in Italy, full of advantages: having light and elastic constructions capable of resisting and dissipating seismic stress, and guaranteeing high physical and acoustic performance.
Source: Light Steel Frame: a new structure for buildings, Incide Engineering
Sustainable models
Deloitte’s analysis suggests implementing low-carbon business models and strategies to accelerate many stages of construction and reduce project costs. For example, incorporating high energy efficiency into buildings helps save significantly on energy costs over their lifetime, but also rethink the way companies buy, sell and collaborate.
Innovation, digital technologies and regulations
In addition to the above-mentioned suggestions, it remains central to utilise all the advantages of BIM and emerging digital technologies to calculate energy use, develop and test logistics plans and optimise water and lighting use. It is useful to implement simulation software for sustainable construction to save energy, resources and reduce project lead times.
Finally, the LEED standard continues to be a driving force behind the increased development of green buildings worldwide. For example, buildings can receive LEED credits for optimising energy performance by analysing efficiency metrics and focusing on load reduction and heating, ventilation and air-conditioning (HVAC) strategies during the design process.
Similarly, construction projects can obtain LEED credits for building operations and maintenance by installing new meters that can be combined to produce data showing the building’s overall energy consumption.
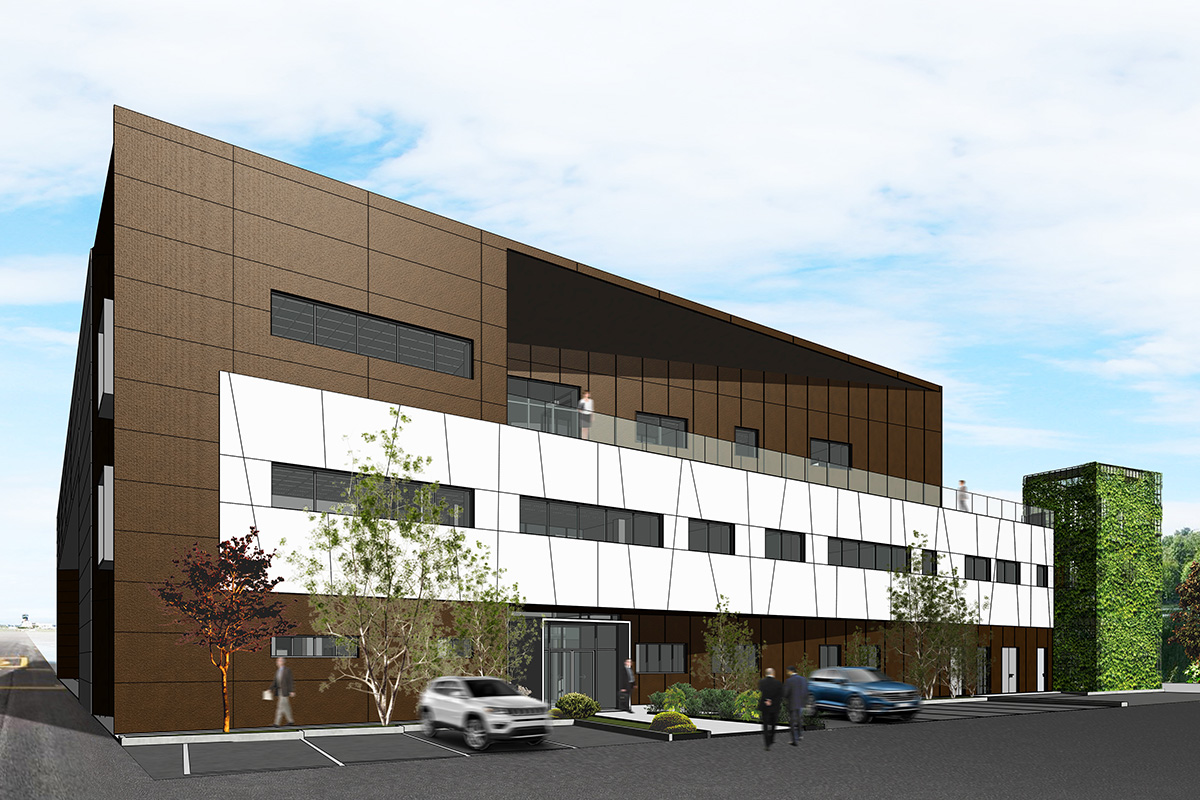
Following this line, Incide Engineering dealt with Hangar PG109 at Ciampino Airport for aircraft maintenance, offices and training areas. In particular, the activity developed from the feasibility study and preliminary and executive BIM design integrated and coordinated between the civil, structures, architectural and MEP disciplines, with computation in Team System CPM, structural and energy calculations, and the design is aimed at LEED certification.
Project: Hangar PG109 Aeroporto Ciampino, Incide Engineering
Deloitte’s report “Sustainable Buildings: Design, Build and Operate to Help Create a Greener Future” is available to download here.